Reference Architecture: Purdue Model and Azure
What Does This Article Cover?
This article will provide a reference architecture focused on enabling Industrial data analysis within Azure.
- General Deployment Guidelines
- Reference Architecture Diagram
- Use Case Overview
- Summary
- Other Resources
General Deployment Guidelines
- It is recommended to install the Intelligence Hub as close to the data source(s) as possible to ensure optimal access to the source data. The occasional unavailability of the output destination can be effectively managed with the Intelligence Hub’s Store and Forward feature. This feature, designed as a failsafe for rare occasions when the output cannot be reached, buffers the data locally in a SQLite database and forwards it once the output target is accessible again. Deploying Intelligence Hub at the edge thus leverages this capability to enhance data integrity and reliability.
- Intelligence Hub is licensed by physical site, 1 license supports unlimited installations for the licensed sites. This enables flexible deployment strategies to deploy the Intelligence Hub by use case, by line or other methods.
- HighByte encourages users to apply the DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself) principal when building use cases in the Intelligence Hub. Ensure Models are built with re-usability in mind. Consider using templating to quickly scale use cases from one point to many.
- When use cases span across multiple sites, HighByte recommends licensing a Central Configuration environment within a data center or cloud environment. This will provide users a single access point to easily manage and distribute configurations.
Reference Architecture Diagram
The following utilizes 2 Professional Intelligence Hub licenses, one for the Intelligence Hub host in Azure cloud, and one for the site deployments in L2 and DMZ. Use cases are focused on connecting, standardizing and contextualizing machines and processing data from OT systems. The architecture utilizes the Purdue model with network segmentation. Please note this is a generalized diagram and many other use case are possible.
This is a generalized diagram and many other use case are possible.
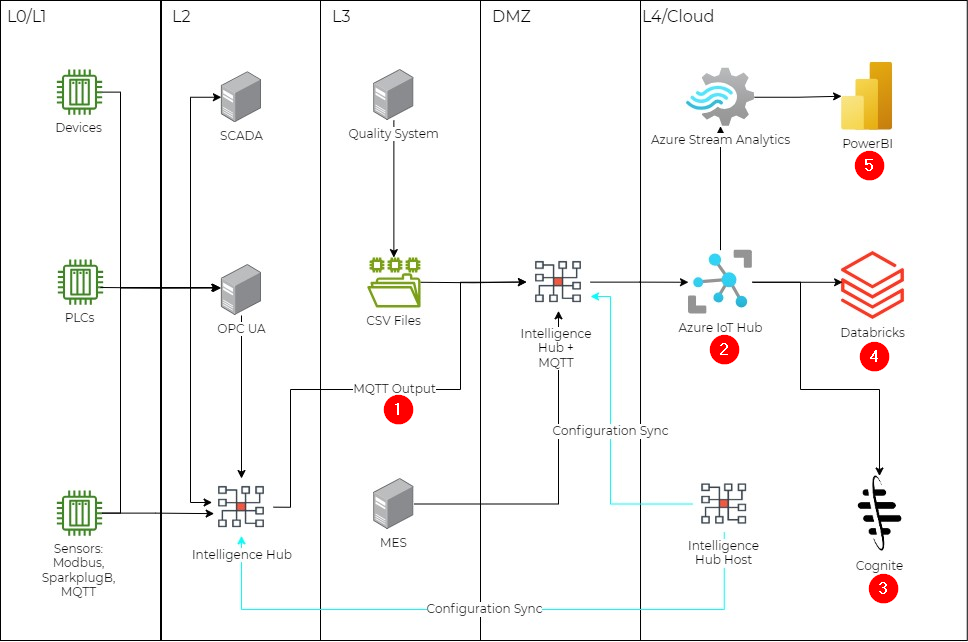
Use Case Overview
This reference architecture utilizes the Intelligence Hub to collect data at various levels of a Purdue model architecture. Utilizing the Hub and Spoke model, customers can deploy multiple Intelligence Hub instances throughout licensed sites to facilitate use case, security and architectural needs.
1. Using Intelligence Hub’s internal MQTT broker: Due to network segmentation, Intelligence Hub is deployed in two locations: L2 and DMZ. The L2 deployment is used to eliminate point to point integrations and enable secure data accessibility to higher network levels.
L0, L1 and L2 data is outputted from the L2 Intelligence Hub to the internal Intelligence Hub broker within the DMZ instance. This data is now available to model together with SCADA and MES data points before outputting to the Enterprise Unified Namespace.
2. Enterprise Unified Namespace: Intelligence Hub outputs data to the enterprise MQTT broker, Azure IoT Hub. This acts as the enterprise Unified Namespace to provide a centralized repository of structured industrial data, in which applications or devices can subscribe or publish data to. Using Dynamic Referencing, we can leverage key attributes from our payload and ensure the outputs automatically generate our ISA-95 hierarchy.
The following could represent a standard output target where each {{this.Attribute}} will extract the value and dynamically build out the MQTT topic structure:
{{this.Site}}/{{this.Area}}/{{this.Line}}/Assets/{{this.AssetType}}/{{this.AssetID}}
Site1/Area1/Line1/Assets/Motor/Motor0013. Cognite: The Hub and Spoke model provides a single integration point into Cognite for all enterprise UNS data. As use cases scale from one to many sites, Cognite can easily consume new payloads of data without establishing a new integration point per site. Users are modeling data at the edge, and delivering standardized and contextualized payloads of data to the enterprise UNS. This approach allows Cognite users to spend less time preparing the data, and more time utilizing the data.
4. Databricks: Data streamed to Databricks to enable machine learning use cases. Focused on predictive analytics, which will increase operational efficiencies and reduce overall costs.
5. PowerBI: Using Azure Stream Analytics, data is delivered to PowerBI which can be used for visualization of key metrics. The consumer of these dashboards could be operational or business personnel to support OEE or preventive maintenance use cases.
Summary
This architecture utilizes a central Intelligence Hub environment within Azure to easily distribute use case configurations from one instance to another. This ensures use cases and common data models are easily distributed to each licensed location via the Central Configuration node. Users can navigate to all remote instances from this one central instance.
This architecture allows data from segmented networks to be securely provided to a central Enterprise Unified Namespace for easy access to industrial data. Consuming systems such as PowerBI, Databricks and Cognite can subscribe to a single integration point to consume and utilize data. This architecture allows for enterprise scale to take successful use cases from one to many sites.